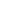What is Roll Roughness? 5 Roll Ra’s and Why They Are Important
Published on January 22, 2020
Roll surface roughness is a critical parameter to consider when creating different products. Having too smooth of a surface can cause problems while having too rough of a surface can cause issues as well. When describing surface roughness, there are many different units that can be used for reference. These values are determined based on the micro-deviations along the length of a surface. We always see what the surface value is for a roll, but why do we choose these roughness values? After we discuss what gives a roll its roughness value, we will give five examples of rolls that require a variety of different roughness’.
Surface Roughness
What is Surface Roughness?
Surface roughness, as defined by Keyence, is a shape that has a variety of peaks and valleys along a shape. If a person were to look at the surface of a material with a microscope, they would see the topographical view of these peaks and valleys. A surface with a larger variation in amplitudes will have a rougher textured surface, whereas a smaller variation will be smoother. By defining a nominal axis for these peaks and valleys to be measured on, numerical values can be given to these points.
What is A Common Unit for Surface Roughness?
There are many different units for defining surface roughness—but roughness average, or Ra, is typically used for standard metal finishes. Ra is always a positive number and is calculated by taking the absolute average deviations over a linear distance. A larger number of deviations will lead to a larger Ra number!
A Little More Technical for Calculating Ra:
As noted in Mikell P. Groover’s textbook Principles of Modern Manufacturing 5th Edition, the mathematical equation for the mean value of roughness is:
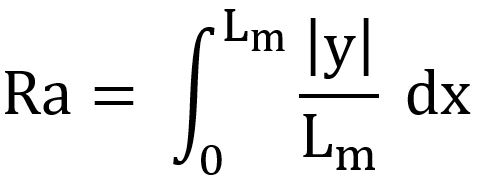
Where:
Ra = Mean roughness value
y = The vertical distance from the defined nominal
Lm = The length of the collection series
This equation can be simplified— allowing for a more visually conceptual understanding:

Where:
n = The nth position along the profile’s length
yi = The vertical distance at the nth position
Figure one gives a more visual understanding of what is happening during the data collection process.
Along the length of the profile, Lm, there are an nth number of height deviations collected along the
length of the profile. Those deviations are collected (at an absolute value) and summed together. The average of these values is what gives the final Ra number. This can be depicted in both micrometers and micro-inches-- depending on capabilities of the measuring tool used.
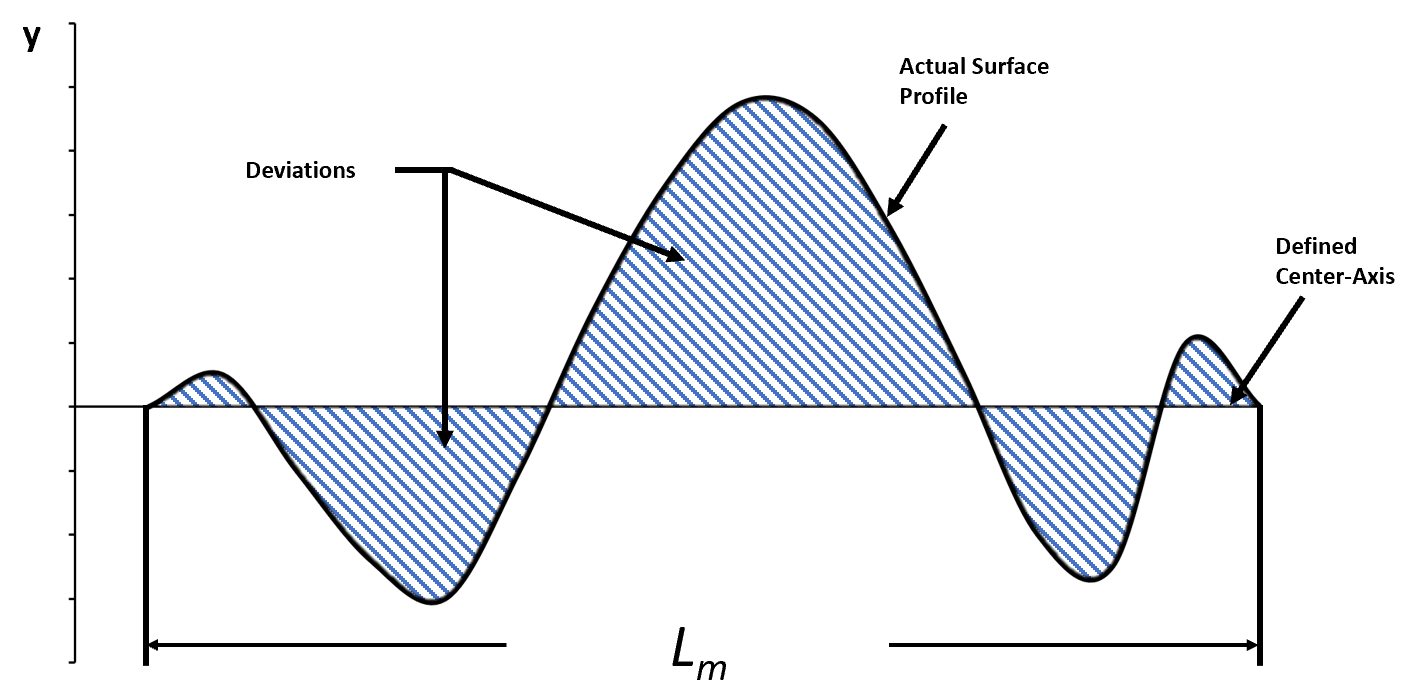
Figure One: Profile Deviations Characterizing Surface Roughness
Ra vs RMS:
Another common roughness unit that may be seen in industry is the root mean
squared, or RMS. Both methods give a representation of roughness, however the RMS will have an inherently larger number than Ra. The way RMS is calculated, any large peak variation can lead to an inflated value, which is why Ra is typically preferred. Check out this link for more information on the difference between Ra and RMS.
Unsure what the roughness of your rolls should be? Contact Precision Roll Grinders for a free consultation on the rolls used in your production process!
Surface Roughness
What is Surface Roughness?
Surface roughness, as defined by Keyence, is a shape that has a variety of peaks and valleys along a shape. If a person were to look at the surface of a material with a microscope, they would see the topographical view of these peaks and valleys. A surface with a larger variation in amplitudes will have a rougher textured surface, whereas a smaller variation will be smoother. By defining a nominal axis for these peaks and valleys to be measured on, numerical values can be given to these points.
What is A Common Unit for Surface Roughness?
There are many different units for defining surface roughness—but roughness average, or Ra, is typically used for standard metal finishes. Ra is always a positive number and is calculated by taking the absolute average deviations over a linear distance. A larger number of deviations will lead to a larger Ra number!
A Little More Technical for Calculating Ra:
As noted in Mikell P. Groover’s textbook Principles of Modern Manufacturing 5th Edition, the mathematical equation for the mean value of roughness is:
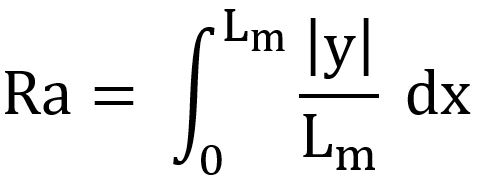
Where:
Ra = Mean roughness value
y = The vertical distance from the defined nominal
Lm = The length of the collection series
This equation can be simplified— allowing for a more visually conceptual understanding:

Where:
n = The nth position along the profile’s length
yi = The vertical distance at the nth position
Figure one gives a more visual understanding of what is happening during the data collection process.
Along the length of the profile, Lm, there are an nth number of height deviations collected along the
length of the profile. Those deviations are collected (at an absolute value) and summed together. The average of these values is what gives the final Ra number. This can be depicted in both micrometers and micro-inches-- depending on capabilities of the measuring tool used.

Figure One: Profile Deviations Characterizing Surface Roughness
Ra vs RMS:
Another common roughness unit that may be seen in industry is the root mean
squared, or RMS. Both methods give a representation of roughness, however the RMS will have an inherently larger number than Ra. The way RMS is calculated, any large peak variation can lead to an inflated value, which is why Ra is typically preferred. Check out this link for more information on the difference between Ra and RMS.
Unsure what the roughness of your rolls should be? Contact Precision Roll Grinders for a free consultation on the rolls used in your production process!